Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service)-AWS Blog Info
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is a scalable, high-speed, low-cost web-based service designed for online backup and archiving of data and application programs. It allows to upload, store, and download any type of files up to 5 GB in size. This service allows the subscribers to access the same systems that Amazon uses to run its own web sites. The subscriber has control over the accessibility of data, i.e. privately/publicly accessible.
- S3 is one of the first services that has been produced by aws.
- S3 stands for Simple Storage Service.
- S3 provides developers and IT teams with secure, durable, highly scalable object storage.
- It is easy to use with a simple web services interface to store and retrieve any amount of data from anywhere on the web.
What is S3?
- S3 is a safe place to store the files.
- It is Object-based storage, i.e., you can store the images, word files, pdf files, etc.
- The files which are stored in S3 can be from 0 Bytes to 5 TB.
- It has unlimited storage means that you can store the data as much you want.
- Files are stored in Bucket. A bucket is like a folder available in S3 that stores the files.
- S3 is a universal namespace, i.e., the names must be unique globally. Bucket contains a DNS address. Therefore, the bucket must contain a unique name to generate a unique DNS address.
If you create a bucket, URL look like:
- If you upload a file to S3 bucket, then you will receive an HTTP 200 code means that the uploading of a file is successful.
Advantages of Amazon S3
- Create Buckets: Firstly, we create a bucket and provide a name to the bucket. Buckets are the containers in S3 that stores the data. Buckets must have a unique name to generate a unique DNS address.
- Storing data in buckets: Bucket can be used to store an infinite amount of data. You can upload the files as much you want into an Amazon S3 bucket, i.e., there is no maximum limit to store the files. Each object can contain upto 5 TB of data. Each object can be stored and retrieved by using a unique developer assigned-key.
- Download data: You can also download your data from a bucket and can also give permission to others to download the same data. You can download the data at any time whenever you want.
- Permissions: You can also grant or deny access to others who want to download or upload the data from your Amazon S3 bucket. Authentication mechanism keeps the data secure from unauthorized access.
- Standard interfaces: S3 is used with the standard interfaces REST and SOAP interfaces which are designed in such a way that they can work with any development toolkit.
- Security: Amazon S3 offers security features by protecting unauthorized users from accessing your data.
S3 is a simple key-value store
S3 is object-based. Objects consist of the following:
- Key: It is simply the name of the object. For example, hello.txt, spreadsheet.xlsx, etc. You can use the key to retrieve the object.
- Value: It is simply the data which is made up of a sequence of bytes. It is actually a data inside the file.
- Version ID: Version ID uniquely identifies the object. It is a string generated by S3 when you add an object to the S3 bucket.
- Metadata: It is the data about data that you are storing. A set of a name-value pair with which you can store the information regarding an object. Metadata can be assigned to the objects in Amazon S3 bucket.
- Subresources: Subresource mechanism is used to store object-specific information.
- Access control information: You can put the permissions individually on your files.
Amazon S3 Concepts
,- Buckets
- Objects
- Keys
- Regions
- Data Consistency Model
- Buckets
- A bucket is a container used for storing the objects.
- Every object is incorporated in a bucket.
- For example, if the object named photos/tree.jpg is stored in the treeimage bucket, then it can be addressed by using the URL http://treeimage.s3.amazonaws.
com/photos/tree.jpg. - A bucket has no limit to the amount of objects that it can store. No bucket can exist inside of other buckets.
- S3 performance remains the same regardless of how many buckets have been created.
- The AWS user that creates a bucket owns it, and no other AWS user cannot own it. Therefore, we can say that the ownership of a bucket is not transferrable.
- The AWS account that creates a bucket can delete a bucket, but no other AWS user can delete the bucket.
- Objects
- Objects are the entities which are stored in an S3 bucket.
- An object consists of object data and metadata where metadata is a set of name-value pair that describes the data.
- An object consists of some default metadata such as date last modified, and standard HTTP metadata, such as Content type. Custom metadata can also be specified at the time of storing an object.
- It is uniquely identified within a bucket by key and version ID.
- Key
- A key is a unique identifier for an object.
- Every object in a bucket is associated with one key.
- An object can be uniquely identified by using a combination of bucket name, the key, and optionally version ID.
- For example, in the URL http://jtp.s3.amazonaws.com/
2019-01-31/Amazons3.wsdl where "jtp" is the bucket name, and key is "2019-01-31/Amazons3.wsdl"
- Regions
- You can choose a geographical region in which you want to store the buckets that you have created.
- A region is chosen in such a way that it optimizes the latency, minimize costs or address regulatory requirements.
- Objects will not leave the region unless you explicitly transfer the objects to another region.
- Data Consistency Model
Amazon S3 replicates the data to multiple servers to achieve high availability.
Two types of model:- Read-after-write consistency for PUTS of new objects.
- For a PUT request, S3 stores the data across multiple servers to achieve high availability.
- A process stores an object to S3 and will be immediately available to read the object.
- A process stores a new object to S3, it will immediately list the keys within the bucket.
- It does not take time for propagation, the changes are reflected immediately.
- Eventual consistency for overwrite PUTS and DELETES
- For PUTS and DELETES to objects, the changes are reflected eventually, and they are not available immediately.
- If the process replaces an existing object with the new object, you try to read it immediately. Until the change is fully propagated, the S3 might return prior data.
- If the process deletes an existing object, immediately try to read it. Until the change is fully propagated, the S3 might return the deleted data.
- If the process deletes an existing object, immediately list all the keys within the bucket. Until the change is fully propagated, the S3 might return the list of the deleted key.
- Read-after-write consistency for PUTS of new objects.
How to Configure S3?
Following are the steps to configure a S3 account.
Step 1 − Open the Amazon S3 console using this link − https://console.aws.amazon.
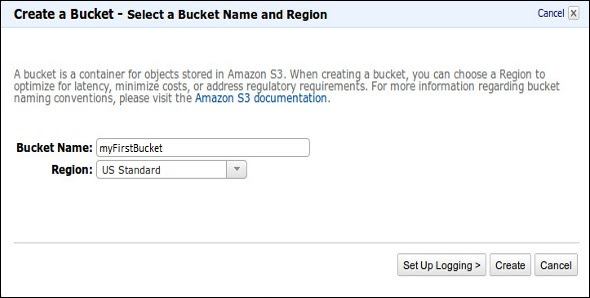
Step 2 − Create a Bucket using the following steps.
A prompt window will open. Click the Create Bucket button at the bottom of the page.
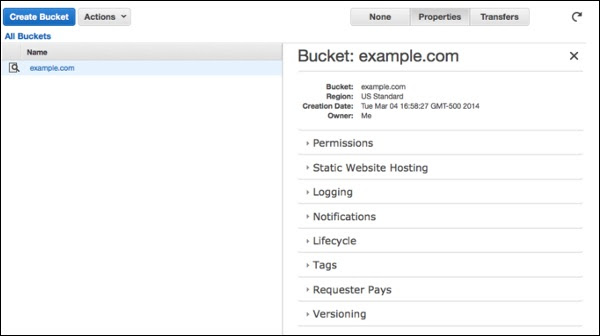
Create a Bucket dialog box will open. Fill the required details and click the Create button.
The bucket is created successfully in Amazon S3. The console displays the list of buckets and its properties.
Select the Static Website Hosting option. Click the radio button Enable website hosting and fill the required details.
Step 3 − Add an Object to a bucket using the following steps.
Open the Amazon S3 console using the following link − https://console.aws.amazon.
com/s3/home Click the Upload button.
Click the Add files option. Select those files which are to be uploaded from the system and then click the Open button.
Click the start upload button. The files will get uploaded into the bucket.
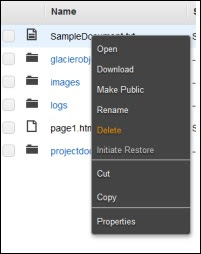
To open/download an object − In the Amazon S3 console, in the Objects & Folders list, right-click on the object to be opened/downloaded. Then, select the required object.
How to Move S3 Objects?
Following are the steps to move S3 objects.
step 1 − Open Amazon S3 console.
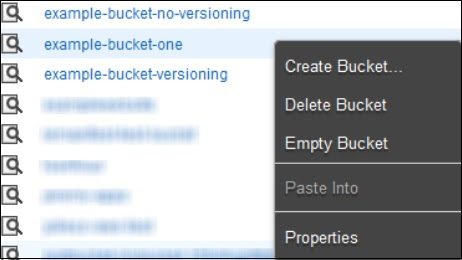
step 2 − Select the files & folders option in the panel. Right-click on the object that is to be moved and click the Cut option.
step 3 − Open the location where we want this object. Right-click on the folder/bucket where the object is to be moved and click the Paste into option.
How to Delete an Object?
Step 1 − Open Amazon S3.
Step 2 − Select the files & folders option in the panel. Right-click on the object that is to be deleted. Select the delete option.
Step 3 − A pop-up window will open for confirmation. Click Ok.
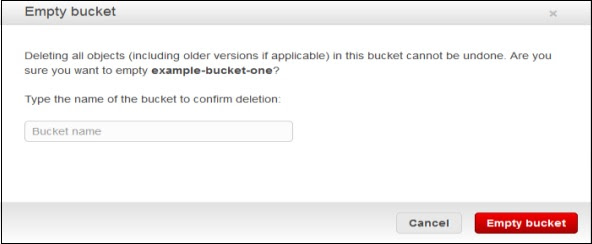
How to Empty a Bucket?
Step 1 − Open Amazon S3 console.
Step 2 − Right-click on the bucket that is to be emptied and click the empty bucket option.
Step 3 − A confirmation message will appear on the pop-up window. Read it carefully and click the Empty bucket button to confirm.
Amazon S3 Features
Low cost and Easy to Use − Using Amazon S3, the user can store a large amount of data at very low charges.
Secure − Amazon S3 supports data transfer over SSL and the data gets encrypted automatically once it is uploaded. The user has complete control over their data by configuring bucket policies using AWS IAM.
Scalable − Using Amazon S3, there need not be any worry about storage concerns. We can store as much data as we have and access it anytime.
Higher performance − Amazon S3 is integrated with Amazon CloudFront, that distributes content to the end users with low latency and provides high data transfer speeds without any minimum usage commitments.
Integrated with AWS services − Amazon S3 integrated with AWS services include Amazon CloudFront, Amazon CLoudWatch, Amazon Kinesis, Amazon RDS, Amazon Route 53, Amazon VPC, AWS Lambda, Amazon EBS, Amazon Dynamo DB, etc.












Comments
Post a Comment